Desi Khand and Bura are both traditional sweeteners that have been used in Indian kitchens for centuries. They are derived from sugarcane juice that is boiled down to a thick syrup and then crystallized. They are coarse-textured and flavorful sugar compounds that are different from the refined white sugar commonly used every day in most parts of the world. Desi khand is also known as khaand, khand, and ‘khandsari’.
To truly understand some basic questions like what is khand? How is it different from sugar? Is brown sugar the same as khand? Can they be considered as true sugar alternatives? Some of these questions will be answered in this blog post for everyone to understand and appreciate what we consume regularly.

In India, Desi Khand and Bura have been used for a long time in cooking, baking, and sweets making, and are considered to be an integral part of Indian cuisine. They are typically associated with traditional Indian celebrations and festivals, such as Diwali, where they are used to make sweets to be enjoyed at home or exchanged among friends and family as gifts. Unfortunately, most Indians have forgotten the use of Desi Khand & Bura which their great-grandmothers used. It is all a case of easy, simple, and convenient. Also whiter the better is the go-to sentiment.

Desi Khand and Bura are often believed to be healthier alternatives to refined sugar, as they retain some of the nutrients found in sugarcane, and have a lower glycemic index. They also impart a unique flavor that can enhance the taste of traditional Indian dishes and sweets. To know more about khand vs sugar and their impact as sugar alternatives, read till the end of the blog.

What’s the difference between Desi Khand, Shakkar, Bura, and Cheeni?
Desi Khand, Shakkar, Bura, and Cheeni are different types of sugar commonly used in India.
- Desi Khand is a type of unrefined cane sugar, which is coarser in texture and darker in color than regular sugar.
- Shakkar has a dark brown color and is another type of unrefined sugar.
- Bura is also unrefined sugar, often produced from sugarcane juice, and has a light cream to pale brown color.
- Cheeni is another name for granulated sugar, which is the most common type of sugar used in cooking and baking.
These different types of sugar are used in various Indian dishes, sweets, and desserts, with each type having its unique taste and color. The difference between khand and sugar also comes from the molasses content, processing, color, flavor & usage. You can read more in the FAQs at the end of the post.

Why Desi Khand and Bura are the Best Sugar Substitutes?
Desi Khand and Bura, being unrefined sugar, may have some health benefits compared to refined sugar:
- Higher nutrient content: Desi Khand and Bura retain some of the minerals and nutrients found in sugarcane, such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, while most of these are lost in the refining process.
- Lower glycemic index: Desi Khand and Bura have a lower glycemic index than refined sugar, which means it is absorbed into the bloodstream more slowly and is less likely to cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- More Flavor: Desi Khand and Bura have a stronger and more complex flavor than refined sugar, due to their coarser texture and higher mineral content, which can enhance the flavor of certain dishes. Indian sweets tend to taste better with strong flavors.
- Better for the environment: The production of Desi Khand and Bura typically uses traditional methods that are more sustainable and have less impact on the environment than the highly industrial methods used to produce refined sugar.
However, it is essential to note that, despite these potential benefits, Desi Khand and Bura still contain a large amount of sugar, and should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Do you want to know if khand and brown sugar are the same? Read on…
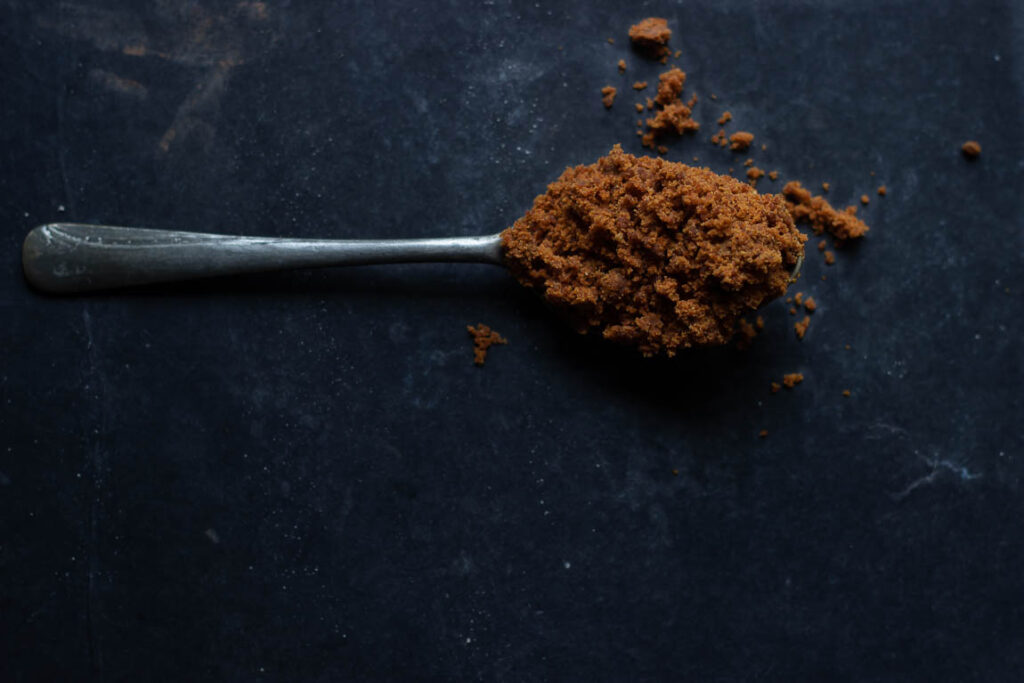

The Best Uses of Desi Khand and Bura
Desi Khand and Bura are commonly used in Indian cooking and baking for their unique flavor and texture:
- For Sweetening drinks: Desi Khand and Bura are commonly used to sweeten Indian beverages such as tea, coffee, and badam milk giving them a rich and complex flavor.
- Baking: They can be used as a sweetener in baked goods, such as cakes, cookies, and bread, to add a distinctive taste and natural color. It goes well with bakes based on clarified butter or ghee or complements Indian cuisine like gulab jamun cake.
- Sweets and desserts: Desi Khand and Bura are often used in traditional Indian sweets and desserts, such as laddu, barfi, and jalebi, to add a rich flavor and natural color.
- Chutneys and sauces: They are sometimes used as a sweetener in Indian chutneys and sauces, such as tamarind and mint chutney, to balance out the tangy and spicy flavors.
- Cooking: They can be used as a sweetener in Indian dishes, such as curries and stews, to add depth and complexity to the flavors. Some cuisines in India also use sugar in most of their savory dishes – like Bengali and Gujarati.

Shelf Life of Desi Khand and Bura
The shelf life of Desi Khand can vary depending on several factors, such as storage conditions, humidity, and exposure to light and air. However, in general, Desi Khand can last for several months when stored in an airtight container in a cool, dry place.
In detail, Desi Khand (unrefined sugar) and Bura (powdered jaggery) have a shelf life greatly affected by storage conditions, but generally:
- Desi Khand:
- Shelf Life: average shelf life is of 1-2 years under suitable conditions.
- Storage: We should store in an airtight container in a cool, dry place. It is best to avoid exposure to moisture, which can cause clumping and spoilage.
- Bura:
- Shelf Life: 6 months to 1 year is considered as an average shelf life of Bura.
- Storage: For best results, store it in an airtight container in a cool, dry place. Ensure it’s kept away from moisture to prevent it from hardening or spoiling.
Optimum storage can extend the shelf life of both Desi Khand and Bura, maintaining their quality and flavor for a longer period of time.

It is important to note that over time, Desi Khand may darken and harden, and its flavor and aroma may change, but it is still safe to consume as long as it does not have any visible signs of spoilage, such as mold or an off odor.

It is recommended to use a clean and dry spoon when scooping Desi Khand from the container to minimize the introduction of moisture, which can shorten its shelf life.
Overall, Desi Khand and Bura are important cultural and culinary elements of Indian tradition, and their use continues to be passed down from generation to generation. They make a good choice as sugar substitutes when possible.

FAQs
Desi Khand, like other forms of sugar, is ideally not recommended for people with diabetes. While it is considered less refined than white sugar and may retain more minerals, it still has a high glycemic index and can raise blood sugar levels.
For managing diabetes, it is generally advised to:
Limit Sugar Intake: Minimize the consumption of all forms of sugar, including Desi Khand.
Monitor Carbohydrates: Pay attention to the total carbohydrate content in your diet, as carbohydrates can impact blood sugar levels.
Choose Low Glycemic Index Foods: Opt for foods with a low glycemic index to help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Consult a Healthcare Provider: Always consult with a healthcare provider or a dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
While Desi Khand may be slightly better than refined sugar in terms of mineral content, it should still be consumed in moderation, especially by individuals with diabetes. They can be considered as sugar alternatives in many use cases.
Desi Khand and Bura are traditional Indian sweeteners. They offer several health benefits as compared to refined white sugar:
Desi Khand benefits are listed below:
1. Less Processed:
Desi Khand is less processed than white sugar, retaining more of the natural molasses and minerals. Due to less processing, it is considered healthier than processed white sugar.
2. Mineral Content:
Khand contains trace amounts of important minerals like calcium, iron, magnesium, and potassium due to minimal processing. This makes khand an important source for the minerals.
3. Lower Glycemic Index:
Desi Khand has a slightly lower glycemic index as compared to refined sugar, which may result in a slower rise in blood sugar levels, although it should still be consumed in moderation.
4. Natural Sweetener:
Being less refined, it is considered a more natural sweetener with fewer chemicals used in its production. The food made using khand has richer flavor, depth of sweetness is also more.
Benefits of using Bura are:
1. Nutrient Retention:
Bura is also a form of unrefined sugar, often produced from sugarcane juice, and has a light cream to pale brown color. It retains more of the nutrients from sugarcane juice, including iron, calcium, and phosphorus.
2. Natural Sweetening Agent:
Bura is made from natural sugarcane or palm sap without extensive chemical processing. So it is a naturally derived sweetener.
3. Rich Flavor:
Bura offers a rich, caramel-like flavor that enhances the taste of traditional sweets and desserts. Indian sweets due to their process of cooking, taste better with strong sweetners than refined sugar.
4. Digestive Benefits:
Bura is also considered to aid digestion and help in cleansing the system, when traditionally consumed in small amounts after meals.
General Benefits of Traditional Sweeteners like Bura & Desi Khand
1. Less Refined:
Both Desi Khand and Bura are less refined compared to white sugar, meaning they undergo fewer chemical processes and retain more of their natural properties. So they retain good properties of the sweetner like mineral content, natural flavor, etc
2. Cultural and Culinary Value:
These sweeteners are integral to many traditional recipes and cultural practices, providing an authentic taste and experience. Due to less processing, they retain a more intese flavor which enhances Indian sweets consumed traditionally in our households.
3. Antioxidant Properties:
The presence of molasses in less refined sugars like Desi Khand can provide some antioxidant benefits, though these are relatively minimal.
While these sweeteners can offer some benefits and can be considered as sugar substitutes, it’s important to remember that they are still forms of sugar and should be consumed in moderation, especially by individuals managing conditions like diabetes.
Khand and sugar are both sweeteners derived from sugarcane. Their difference lies in the processing and composition of each. Khand undergoes less processing and hence retains natural molasses whereas, for easy consumption, appearance, and increased shelf life, refined sugar particularly undergoes extensive processing to produce a pure sucrose product.
While both khaand & sugar are derivatives of sugarcane, they differ in their processing and their resultant composition. Khaand retains natural molasses due to lesser processing while refined sugar is almost pure sucrose, with little to no molasses content.
Khand & brown sugar are not the same but do share some similarities, for example:
1. Processing: Both khaand & brown sugar undergo lesser processing than refined sugar. Khand is made from minimal processing from sugarcane while brown sugar is refined white sugar with some molasses reintroduced for the color, texture & taste.
2. Color & Flavor: Both khand & sugar have a brown color due to the presence of molasses. They also have a richer taste and flavor because of the presence of molasses.
3. Molasses Content: Khaand retains more molasses as compared to brown sugar. Though molasses in khand is natural as it undergoes lesser processing. Brown sugar, on the other hand, is refined white sugar where some molasses is added back during processing. The molasses content in brown sugar depends on manufacturer/ brand to brand.
4. Usage: Khand is a traditional form of unrefined sugar used in many Indian sweets & desserts. Brown sugar, however, is used globally and can be easily used as an alternative to refined sugar in various recipes, especially baking & cooking where its flavor & color can enhance the dish.
Khaand and sugar differ in their processing, color, flavor, molasses content, and ultimate usage. While they both are produced from sugarcane, khand is rich in natural molasses, less processed, brown in color, deep in flavor, and largely used as a traditional sweetener in Indian recipes perfected by our grandmothers. On the other hand, sugar is refined, white in color, has minimal to zero molasses, and is used globally in various dishes including baking and cooking recipes which require uniform taste.
Brown sugar and desi khand are derivatives of sugarcane. For making brown sugar, some amount of molasses is added back to the refined sugar, while desi khand retains natural molasses and minerals due to lesser processing. Desi khand is richer in flavor as compared to brown sugar due to natural molasses. This rich flavor makes it ideal to be used in Indian sweets and dishes while brown sugar suits global cooking making it a suitable choice for all types of diverse food.
Khand/ khaand is an unrefined, unprocessed sugar traditionally made in India. It is also known as “khandsari” or “desi khand.” Even today in villages or small towns, Khand is produced by boiling sugarcane juice to form a thick syrup, which is then allowed to cool and solidify into blocks or cones. This age-old method involves minimal processing compared to refined white sugar production on a mass scale, allowing khaand to retain some natural molasses and minerals present in sugarcane juice. Hence Khand derived traditionally has a light brown color and a slightly rich & strong flavor compared to refined white sugar. It is commonly used in Indian cuisine and traditional sweets like bajre ki kheer, rabri, kadha doodh, etc.